Search and Find
Service
Dendritic Spines
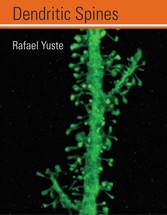
Most neurons in the brain are covered by dendritic spines, small protrusions that arise from dendrites, covering them like leaves on a tree. But a hundred and twenty years after spines were first described by Ramon y Cajal, their function is still unclear. Dozens of different functions have been proposed, from Cajal's idea that they enhance neuronal interconnectivity to hypotheses that spines serve as plasticity machines, neuroprotective devices, or even digital logic elements. In Dendritic Spines, leading neurobiologist Rafael Yuste attempts to solve the ",spine problem,", searching for the fundamental function of spines. He does this by examining many aspects of spine biology that have fascinated him over the years, including their structure, development, motility, plasticity, biophysical properties, and calcium compartmentalization. Yuste argues that we may never understand how the brain works without understanding the specific function of spines. In this book, he offers a synthesis of the information that has been gathered on spines (much of which comes from his own studies of the mammalian cortex), linking their function with the computational logic of the neuronal circuits that use them. He argues that once viewed from the circuit perspective, all the pieces of the spine puzzle fit together nicely into a single, overarching function. Yuste connects these two topics, integrating current knowledge of spines with that of key features of the circuits in which they operate. He concludes with a speculative chapter on the computational function of spines, searching for the ultimate logic of their existence in the brain and offering a proposal that is sure to stimulate discussions and drive future research.
All prices incl. VAT